Last Updated on April 21, 2025
AP Chemistry Exam Unit 5 Practice Test (Kinetics) 2025. Try our AP Chemistry Unit 5: Atomic Structure and Properties Multiple Choice Questions and Answers and Free-Response Questions for free. This unit is 7%–9% of the Advanced Placement (AP) Exam score.
You’ll explore various questions related to methods for observing the changes that occur during a chemical reaction, the factors that influence reaction rate, and how these factors relate to a series of elementary reactions. This online quiz engages subject reviews, covering topics from Reaction rate to Catalysis.
AP Chemistry Exam Unit 5 Practice Test
Free-Response Questions
a) In the gas phase at 500 °C, cyclopropane, C3H6, reacts to form propane in a first-order reaction.
(i) Given the following data, plot the ln[C3H6] versus time on the grid provided.
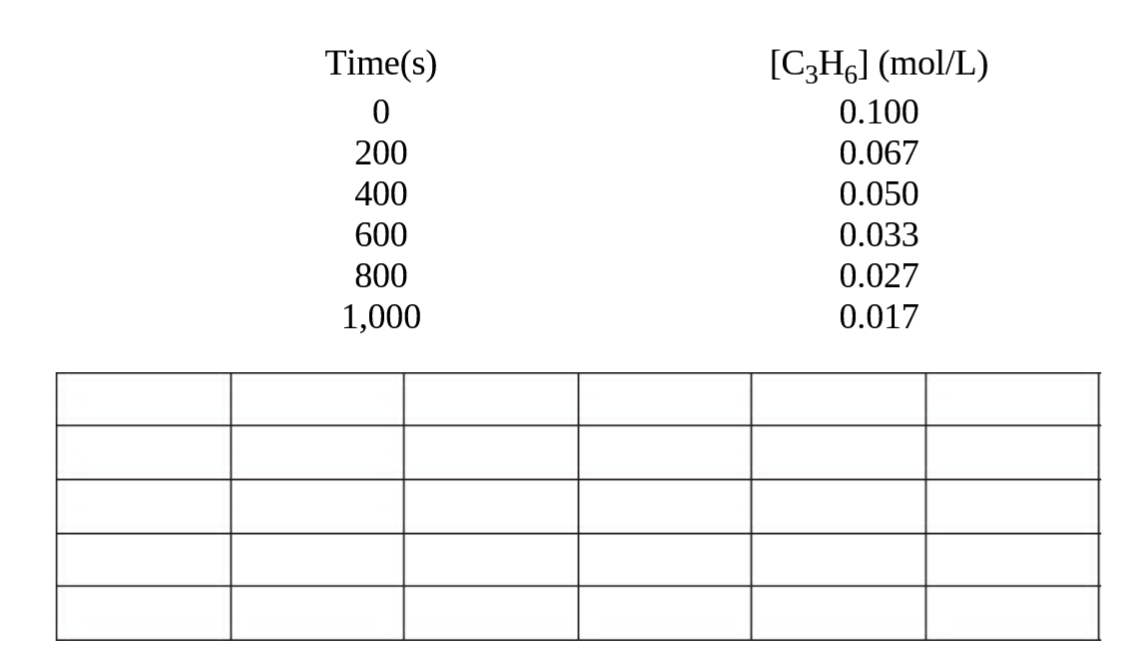
(ii) How does this plot verify that the reaction is first order? Justify your answer.
(iii) What is the rate constant for this reaction?
(b) You are given the following reaction and the table of data below.
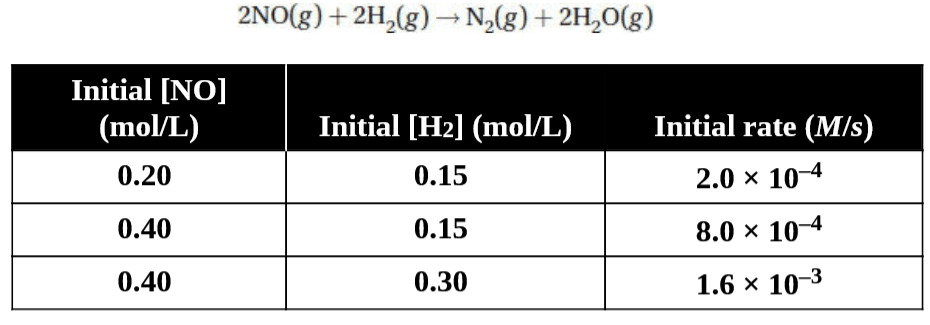
(i) Determine the rate law for this reaction.
(ii) What is the value of the rate constant for this reaction?
See also:
Unit Wise Practice Test- Unit 1: Atomic Structure and Properties
- Unit 2: Compound Structure and Properties
- Unit 3: Properties of Substances and Mixtures
- Unit 4: Chemical Reactions
- Unit 5: Kinetics
- Unit 7: Equilibrium
- Unit 8: Acids and Bases
- Unit 9: Thermodynamics and Electrochemistry
