Last Updated on March 28, 2025
EKG Rhythm Strips Practice Pre Test 2025: NHA (National Healthcareer Association) It will help you in nursing, NHA EKG Technician, EKG certification exam, and ACLS course prep. Try our free EKG Rhythm Strips questions and answers online.
EKG Rhythm Strips Practice Pre Test 2025
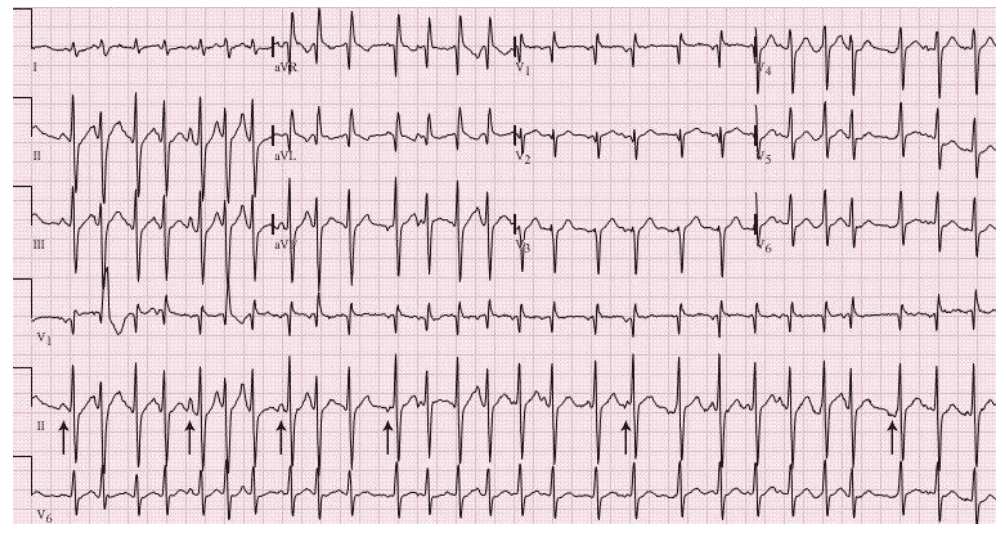
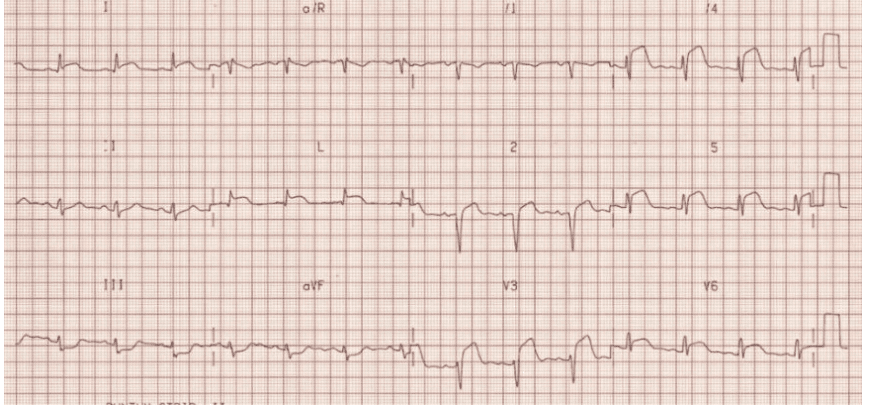
Q1. A thirty-five-year-old person presents with tremors. He’s been ingesting heavily with close friends this past weekend. This is usually his ECG. Current your findings in addition to give a medical diagnosis.
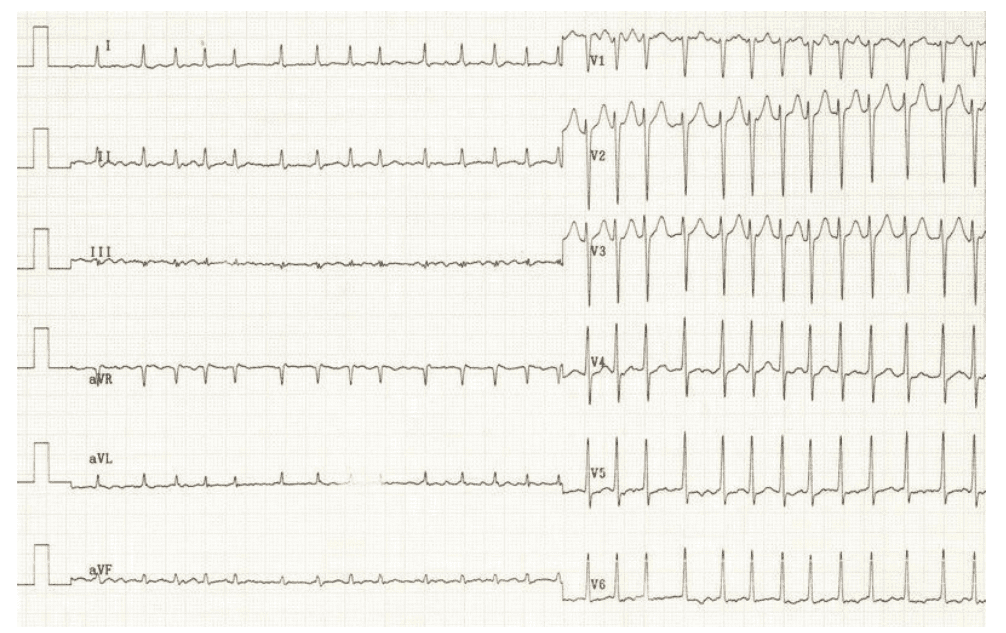
Rate: ______
Rhythm Irregularly: _____
Axis: ____
PR/P-wave: ____
QRS: ____
ST/T-wave: _____
QTc/other: ____
Diagnosis: ________
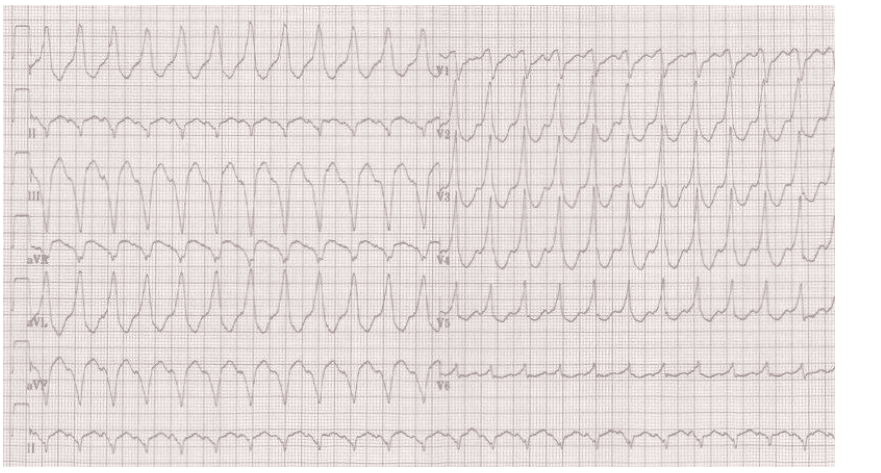
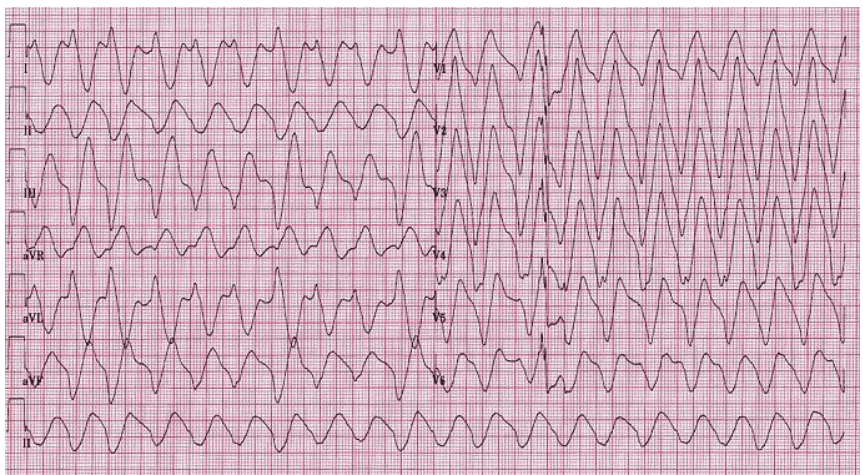
Q2. A 45 yr old businessman offers an experience that his center is racing. He or she has some lack of breath. This is certainly his ECG. Current your findings and offer a diagnosis.
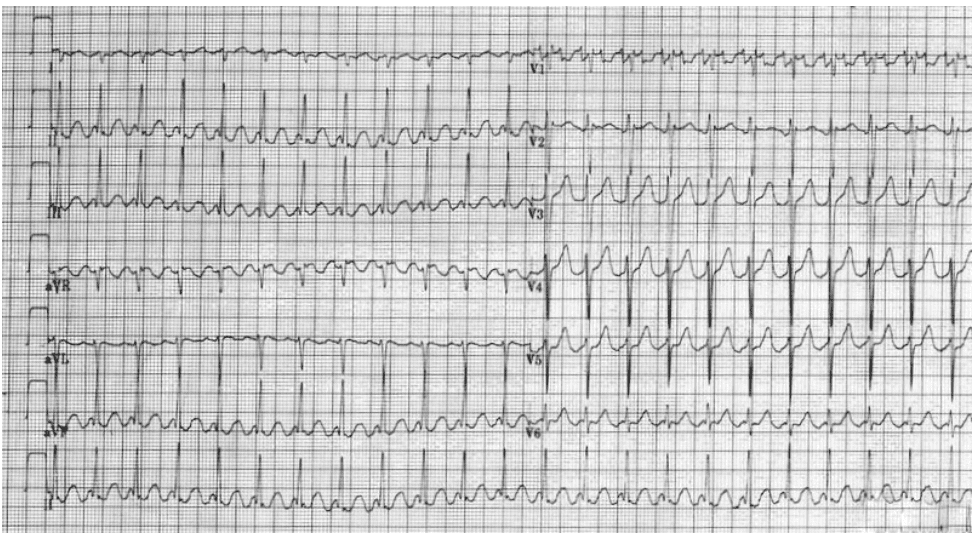
Rate: ______
Rhythm Irregularly: _____
Axis: ____
PR/P-wave: ____
QRS: ____
QTc/other: ____
Diagnosis: ________
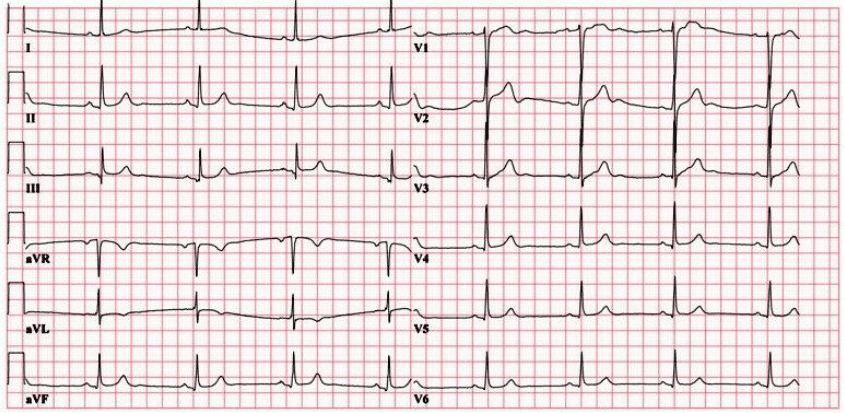
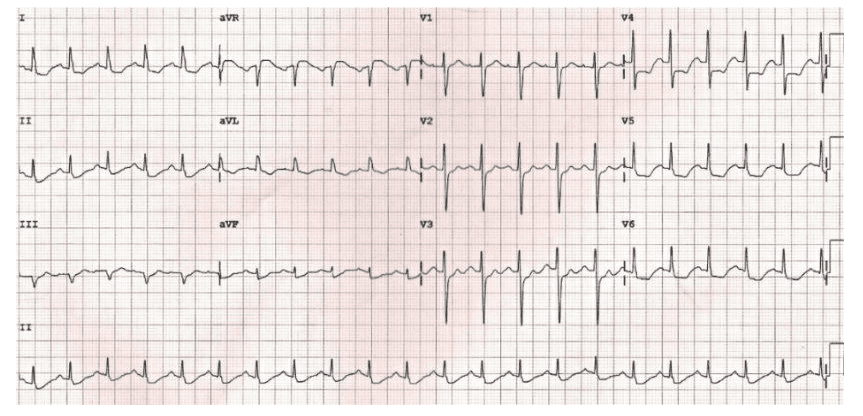
Q3. A 75-year-old man with a history of COPD presents with fever and increased sputum production. An ECG is taken in the emergency department. What does it show?
Rate: ______
Rhythm Irregularly: _____
Axis: ____
PR/P-wave: ____
QRS: ____
ST/T-wave: _____
QTc/other: ____
Diagnosis: ________
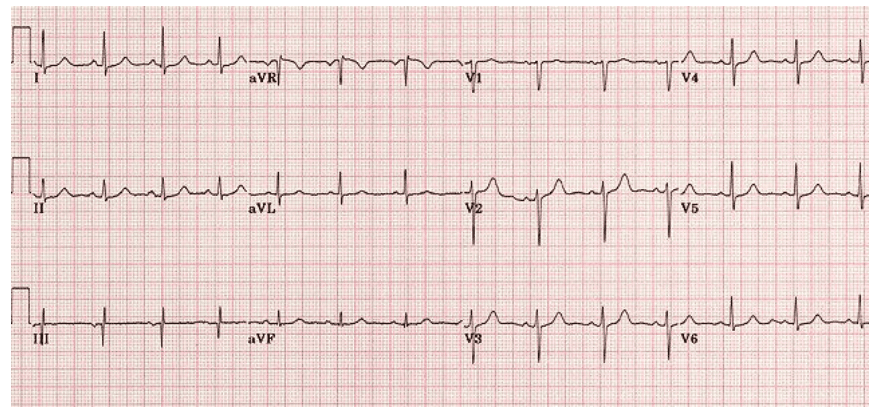
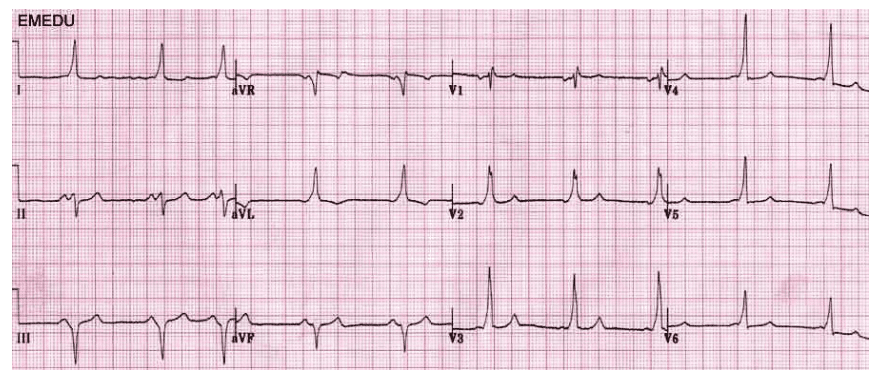
Q4. A fit and well 31-year-old man presents for a routine insurance medical. This is his ECG. Present your findings and give the diagnosis.
Rate: ______
Rhythm Irregularly: _____
Axis: ____
PR/P-wave: ____
QRS: ____
ST/T-wave: _____
QTc/other: ____
Diagnosis: ________
Q5. A 65-year-old man with a history of ischemic heart disease is found unresponsive. He has no central pulse and is making no respiratory effort. This is his ECG. What is the diagnosis and what will you do?
Rate: ______
Rhythm Irregularly: _____
Axis: ____
PR/P-wave: ____
QRS: ____
ST/T-wave: _____
QTc/other: ____
Diagnosis: ________
Q6. A 72-year-old lady presents with collapse. This is her ECG. Present your findings. How would you proceed?
Rate: ______
Rhythm Irregularly: _____
Axis: ____
PR/P-wave: ____
QRS: ____
ST/T-wave: _____
QTc/other: ____
Q7. A 62-year-old person presents with restricted core chest soreness radiating to his / her left shoulder. This specific is his first ECG. Present your current findings and offer an analysis.
Rate: ______
Rhythm Irregularly: _____
Axis: ____
PR/P-wave: ____
QRS: ____
ST/T-wave: _____
QTc/other: ____
Q8. A 55-year-old renal dialysis patient presents to the emergency department having missed his last session of dialysis due to feeling dizzy and unwell. This is his ECG. Present your findings and give a diagnosis.
Rate: ______
Rhythm Irregularly: _____
Axis: ____
PR/P-wave: ____
QRS: ____
ST/T-wave: _____
QTc/other: ____
Q9. A 65-year-old woman presents with chest pain radiating to her jaw and down her left arm. It feels like her ‘normal’ angina nevertheless at this juncture it provides not eased together with GTN spray. This specific is her ECG. Present your conclusions and give typically the diagnosis.
Rate: ______
Rhythm Irregularly: _____
Axis: ____
PR/P-wave: ____
QRS: ____
ST/T-wave: _____
QTc/other: ____
Q10. A 25-year-old man offers with a failure which occurred when he was playing in a football match. He’s suffered episodes of fainting in typically the past. This is certainly his / her ECG. Is it usually a medical diagnosis?
Rate: ______
Rhythm Irregularly: _____
Axis: ____
PR/P-wave: ____
QRS: ____
ST/T-wave: _____
QTc/other: ____
See also:
- FREE EKG Practice Test 2025 Official Study Guide PDF]
- EKG Multiple Choice Questions Answers
- EKG Rhythm Strips Practice Test 2024
- EKG Practice Test for the Nurse Practitioner and Physician Assistant