Last Updated on January 17, 2025
Communication and Network Security Question CISSP Course: Try this CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional) sample review practice test on Chapter 4: Communication and Network Security for ISC CISSP certification preparation.
Communication and Network Security (Domain 4)
SUBDOMAINS:
- Assess and implement secure design principles in network architectures
- Secure network components
- Implement secure communication channels according to design
Communication and Network Security Questions
Q1. Gary wants to distribute a large file and prefers a peer-to-peer CDN. Which of the following is the most common example of this type of technology?
- A. CloudFlare
- B. BitTorrent
- C. Amazon CloudFront
- D. Akamai Edge
Q2. During a wireless network security assessment, Jim discovers that LEAP is in use on a network using WPA. What recommendation should Jim make?
- A. Continue to use LEAP. It provides better security than TKIP for WPA networks.
- B. Use an alternate protocol like PEAP or EAP-TLS and implement WPA2 if supported.
- C. Continue to use LEAP to avoid authentication issues, but move to WPA2.
- D. Use an alternate protocol like PEAP or EAP-TLS, and implement Wired Equivalent Privacy to avoid wireless security issues.
Q3. Ben has connected his laptop to his tablet PC using an 802.11ac connection. What wireless network mode has he used to connect these devices?
- A. Infrastructure mode
- B. Wired extension mode
- C. Ad hoc mode
- D. Standalone mode
Q4. Selah’s and Nick’s PCs simultaneously send traffic by transmitting simultaneously. What network term describes the range of systems on a network that could be affected by this same issue?
- A. The subnet
- B. The supernet
- C. A collision domain
- D. A broadcast domain
Q5. Sarah is manually reviewing a packet capture of TCP traffic and finds that a system is setting the RST flag in the TCP packets it repeatedly sends during a short period of time. What does this flag mean in the TCP packet header?
- A. RST flags mean “Rest.” The server needs traffic to briefly pause.
- B. RST flags mean “Relay-set.” The packets will be forwarded to the address set in the packet.
- C. RST flags mean “Resume Standard.” Communications will resume in their normal format.
- D. RST means “Reset.” The TCP session will be disconnected.
- A. 802.11a
- B. 802.11g
- C. 802.11n
- D. 802.11ac
- A. TFTP
- B. HFTPS
- C. SecFTP
- D. SFTP
- A. IP addresses
- B. TCP and UDP protocols
- C. MAC addresses
- D. Sending and receiving bits via hardware
- A. If the devices have vendor support
- B. If the devices are under warranty
- C. If major devices support redundant power supplies
- D. If all devices support redundant power supplies
- A. PAP
- B. CHAP
- C. EAP
- D. LEAP
Q11. Which one of the following protocols is commonly used to provide back-end authentication services for a VPN?
- A. HTTPS
- B. RADIUS
- C. ESP
- D. AH
Q12. Isaac wants to ensure that his VoIP session initialization is secure. What protocol should he ensure is enabled and required?
- A. SVOIP
- B. PBSX
- C. SIPS
- D. SRTP
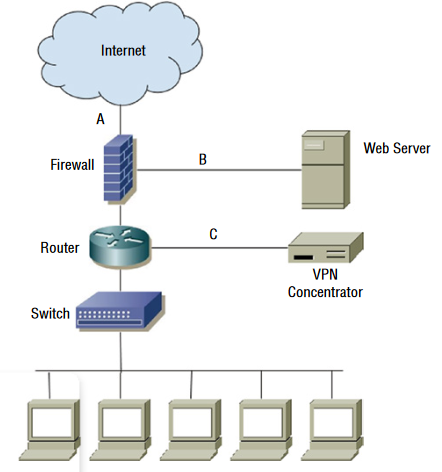
For questions 13–15, please refer to the following scenario and diagram: Chris is designing layered network security for his organization.
Q13. What type of firewall design is shown in the diagram?
- A. A single-tier firewall
- B. A two-tier firewall
- C. A three-tier firewall
- D. A four-tier firewall
Q14. If the VPN grants remote users the same access to network and system resources as local workstations have, what security issue should Chris raise?
- A. VPN users will not be able to access the web server.
- B. There is no additional security issue; the VPN concentrator’s logical network location matches the logical network location of the workstations
- C. Web server traffic is not subjected to stateful inspection.
- D. VPN users should only connect from managed PCs.
Q15. If Chris wants to stop cross-site scripting attacks against the web server, what is the best device for this purpose, and where should he put it?
- A. A firewall, location A
- B. An IDS, location A
- C. An IPS, location B
- D. A WAF, location C
Q16. Susan is deploying a routing protocol that maintains a list of destination networks with metrics that include the distance in hops to them and the direction traffic should be sent to them. What type of protocol is she using?
- A. A link-state protocol
- B. A link-distance protocol
- C. A destination metric protocol
- D. A distance-vector protocol
Q17. Ben has configured his network to not broadcast an SSID. Why might Ben disable SSID broadcast, and how could his SSID be discovered?
- A. Disabling SSID broadcast prevents attackers from discovering the encryption key. The SSID can be recovered from decrypted packets.
- B. Disabling SSID broadcast hides networks from unauthorized personnel. The SSID can be discovered using a wireless sniffer.
- C. Disabling SSID broadcast prevents issues with beacon frames. The SSID can be recovered by reconstructing the BSSID.
- D. Disabling SSID broadcast helps avoid SSID conflicts. The SSID can be discovered by attempting to connect to the network.
Q18. What network tool can be used to protect the identity of clients while providing Internet access by accepting client requests, altering the source addresses of the requests, mapping requests to clients, and sending the modified requests out to their destination?
- A. A switch
- B. A proxy
- C. A router
- D. A firewall
Q19. Susan wants to secure her communications traffic via multiple internet service providers as it is sent to her company’s second location. What technology should she use to protect the traffic for an always on, always connected link between the sites?
- A. FCoE
- B. SDWAN
- C. A point-to-point IPsec VPN
- D. Zigbee
Q20. Melissa wants to combine multiple physical networks in her organization in a way that is transparent to users but allows the resources to be allocated as needed for networked services. What type of network should she deploy?
- A. iSCSI
- B. A virtual network
- C. SDWAN
- D. A CDN
See also:
- FREE CISSP Practice Test 2025 Official Study Guide [PDF]
- Security and Risk Management Practice Test
- Asset Security Practice Test
- Security Architecture and Engineering Practice Test
- Communication and Network Security Practice Test
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) Practice Test
- Security Assessment and Testing Practice Test
- Security Operations Practice Test
- Software Development Security Practice Test