Last Updated on January 17, 2025
Security Operations Question CISSP Course: Try CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional) sample review practice test in Chapter 7: Security Operations for ISC CISSP certification preparation.
Security Operations
- Understand and comply with investigations
- Conduct logging and monitoring activities
- Perform Configuration Management (CM) (e.g., provisioning, baselining, automation)
- Apply foundational security operations concepts
- Apply resource protection
- Conduct incident management
- Operate and maintain detective and preventative measures
- Implement and support patch and vulnerability management
- Understand and participate in change managementprocesses
- Implement recovery strategies
- Implement Disaster Recovery (DR) processes
- Test Disaster Recovery Plans (DRP)
- Participate in Business Continuity (BC) planning and exercises
- Implement and manage physical security
- Address personnel safety and security concerns
Security Operations Question CISSP Course
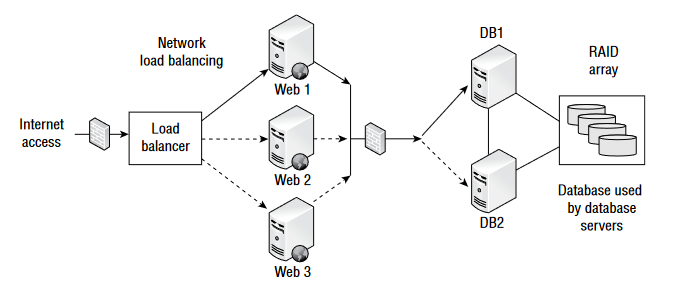
Q1. Mary is reviewing the availability controls for the system architecture shown here. What technology is shown that provides fault tolerance for the database servers?
- A. Failover cluster
- B. UPS
- C. Tape backup
- D. Cold site
Q2. Joe is the security administrator for an ERP system. He is preparing to create accounts for several new employees. What default access should he give to all of the new employees as he creates the accounts?
- A. Read only
- B. Editor
- C. Administrator
- D. No access
Q3. Tim is configuring a privileged account management solution for his organization. Which one of the following is not a privileged administrative activity that should be automatically sent to a log of superuser actions?
- A. Purging log entries
- B. Restoring a system from backup
- C. Logging into a workstation
- D. Managing user accounts
Q4. When one of the employees of Alice’s company calls in for support, she uses a code word that the company agreed to use if employees were being forced to perform an action. What is this scenario called?
- A. Social engineering
- B. Duress
- C. Force majeure
- D. Stockholm syndrome
Q5. Jordan is preparing to bring evidence into court after a cybersecurity incident investigation. He is responsible for preparing the physical artifacts, including affected servers and mobile devices. What type of evidence consists entirely of tangible items that may be brought into a court of law?
- A. Documentary evidence
- B. Parol evidence
- C. Testimonial evidence
- D. Real evidence
Q6. Lauren wants to ensure that her users only run software that her organization has approved. What technology should she deploy?
- A. Blacklisting
- B. Configuration management
- C. Whitelisting
- D. Graylisting
Q7. Colin is responsible for managing his organization’s use of cybersecurity deception technologies. Which one of the following should he use on a honeypot system to consume an
attacker’s time while alerting administrators?
- A. Honeynet
- B. Pseudoflaw
- C. Warning banner
- D. Darknet
Q8. Toni responds to the desk of a user who reports slow system activity. Upon checking out- bound network connections from that system, Toni notices a large amount of social media traffic originating from the system. The user does not use social media, and when Toni checks the accounts in question, they contain strange messages that appear encrypted. What is the most likely cause of this traffic?
- A. Other users are relaying social media requests through the user’s computer.
- B. The user’s computer is part of a botnet.
- C. The user is lying about her use of social media.
- D. Someone else is using the user’s computer when she is not present.
Q9. John deploys his website to multiple regions using load balancers around the world through his cloud infrastructure as a service provider. What availability concept is he using?
- A. Multiple processing sites
- B. Warm sites
- C. Cold sites
- D. A honeynet
Q10. Jim would like to identify compromised systems on his network that may be participating in a botnet. He plans to do this by watching for connections made to known command-and-control servers. Which one of the following techniques would be most likely to provide this information if Jim has access to a list of known servers?
- A. NetFlow records
- B. IDS logs
- C. Authentication logs
- D. RFC logs
For questions 11–15, please refer to the following scenario:
Gary was recently hired as the first chief information security officer (CISO) for a local government agency. The agency recently suffered a security breach and is attempting to build a new information security program. Gary would like to apply some best practices for secu- rity operations as he is designing this program.
Q11. As Gary decides what access permissions he should grant to each user, what principle should guide his decisions about default permissions?
- A. Separation of duties
- B. Least privilege
- C. Aggregation
- D. Separation of privileges
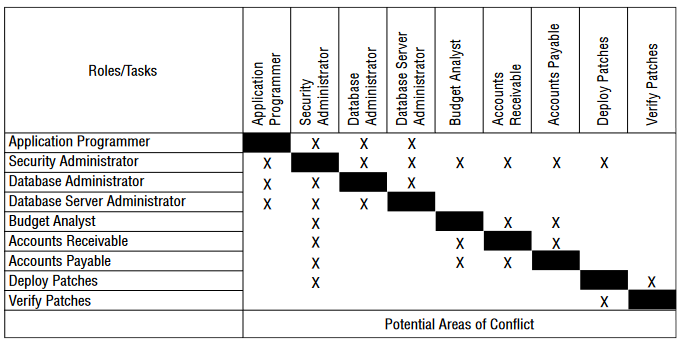
Q12. As Gary designs the program, he uses the matrix shown here. What principle of information security does this matrix most directly help enforce?
- A. Segregation of duties
- B. Aggregation
- C. Two-person control
- D. Defense in depth
Q13. Gary is preparing to create an account for a new user and assign privileges to the HR database. What two elements of information must Gary verify before granting this access?
- A. Credentials and need to know
- B. Clearance and need to know
- C. Password and clearance
- D. Password and biometric scan
Q14. Gary is preparing to develop controls around access to root encryption keys and would like to apply a principle of security designed specifically for very sensitive operations. Which principle should he apply?
- A. Least privilege
- B. Defense in depth
- C. Security through obscurity
- D. Two-person control
Q15. How often should Gary and his team review the privileged access a user has to sensitive systems? (Select all that apply.)
- A. On a periodic basis
- B. When a user leaves the organization
- C. When a user changes roles
- D. On a daily basis
Q16. Which one of the following terms is often used to describe a collection of unrelated patches released in a large collection?
- A. Hotfix
- B. Update
- C. Security fix
- D. Service pack
Q17. Tonya is collecting evidence from a series of systems that were involved in a cybersecurity incident. A colleague suggests that she use a forensic disk controller for the collection process. What is the function of this device?
- A. Masking error conditions reported by the storage device
- B. Transmitting write commands to the storage device
- C. Intercepting and modifying or discarding commands sent to the storage device
- D. Preventing data from being returned by a read operation sent to the device
Q18. Lydia is processing access control requests for her organization. She comes across a request where the user does have the required security clearance, but there is no business justification for the access. Lydia denies this request. What security principle is she following?
- A. Need to know
- B. Least privilege
- C. Separation of duties
- D. Two-person control
Q19. Helen is tasked with implementing security controls in her organization that might be used to deter fraudulent insider activity. Which one of the following mechanisms would be LEAST useful to her work?
- A. Job rotation
- B. Mandatory vacations
- C. Incident response
- D. Two-person control
Q20. Matt wants to ensure that critical network traffic from systems throughout his company is prioritized over web browsing and social media use at this company. What technology can he use to do this?
- A. VLANs
- B. QoS
- C. VPN
- D. ISDN
See also:
- FREE CISSP Practice Test 2025 Official Study Guide [PDF]
- Security and Risk Management Practice Test
- Asset Security Practice Test
- Security Architecture and Engineering Practice Test
- Communication and Network Security Practice Test
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) Practice Test
- Security Assessment and Testing Practice Test
- Security Operations Practice Test
- Software Development Security Practice Test